Performance tuning / resource management
This guide gives you information on how to configure Ozeki NG SMS Gateway for high performance and for long term operation. It gives you some information about the internal architecture of the product, to help you understand how it works. The guide covers the following resource management areas: Memory, CPU.
Introduction
It is important to understand that high performance comes at a cost. A system that can send and receive a lot messages cannot do as much as a system that provides a smaller throughput. To get better performance, you have to give up some comfortable features, such as keeping your messages for a long time in the gateway and detailed logging.
We should also state that a performance of a software largely depends on the underlying hardware. You can increase performance by installing the product to a more powerful hardware. Ozeki NG uses threads and memory. To get better performance it is important to have large amount of memory in the system and it is ideal to run the software on dual or quad core processors or multiprocessor hardware.
Of course we should not forget, that the speed of a software is also effected by other software entities running on the same computer. For example if you have a database server such as Oracle and an SMS server such as Ozeki NG running on the same hardware resources must be shared. It is better to put the two services on different computers (even if you have an SQL SMS gateway configuration). An SMS server communicating with a database server over a high speed network connection can be significantly faster then if the two services are running on the same hardware and are fighting for resources such as memory and disk access.
Memory
Symptom:If you use Ozeki NG for a long time, you might notice, that the amount of memory used is increasing.
Reason:The messages stored in the system are cached in memory for better performance. As you use the system more and more messages and message references will be stored.
Solution:To solve the problem of increasing memory usage, you should configure the system to delete old messages. This will speed up the system and will put a limit to the maximum number of memory used. (To save a long term history of sent and received messages, we suggest you to setup SQL logging.)
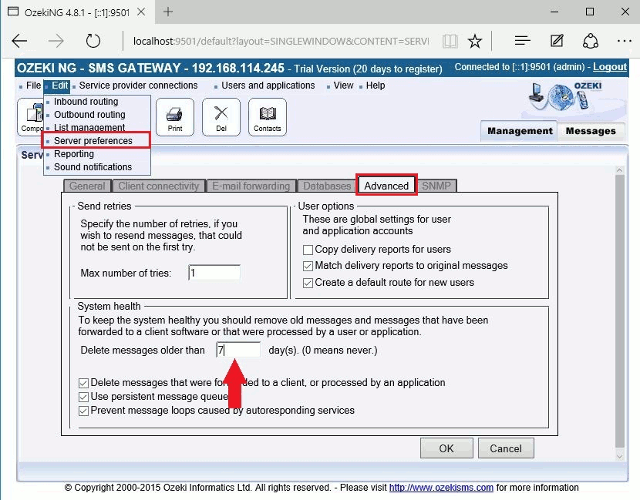
To configure the deletion of old messages open the Server preferences form in the Edit menu. Then select Advanced tab and in System health enter a number greater than 0 into the "Delete messages older than" field (Figure 1). I recommend you to keep your messages for 7 days because a returned delivery report can only be matched to the appropriate sent messages if the sent message still exists in the system.
CPU
Question:How can I optimize for performance?
Understand what happens:
To optimize your SMS gateway for speed you have to decrease the amount of tasks per message. When Ozeki NG SMS gateway sends an SMS message, the following actions are taken:
1.) The message is accepted for delivery
1/a. It is verified to see if correct message format and correct
telephone number format is used
1/b. A log file entry is written to the log file belonging to the user
who sent the message mark that the message is accepted for delivery
1/c. The message is saved into the outbox queue. If this queue is persistent
the message is saved to the disk.
2.) Routing
2/a. A message is taken from the outbox queue.
2/b. A routing decision is made to select the appropriate service provider
2/c. A log file entry is written into the system event log to mark the
routing decision
2/d. The appropriate service provider is selected
3.) The message is sent
3/a. The message is transmitted
3/b. The message reference (callback id) returned by the provider is registered
3/g. A log file entry is written to the log file belonging to the service
provider connection
4.) Message delivery is administrated
4/a. The user who sent the message is notified about the
"delivered to network" state
4/b. A log file entry is written to the user log file
Do the optimization:
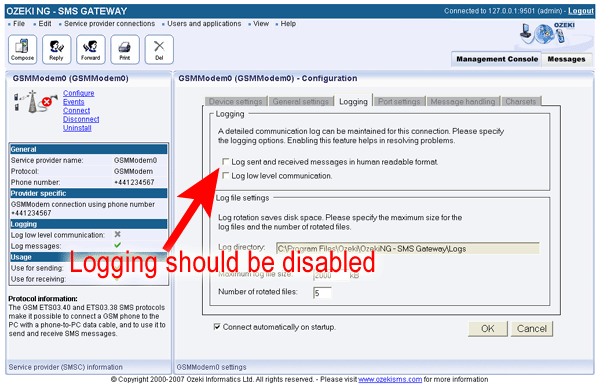
The first (most important) step you should take is to decrease the amount of disk usage. This can be done if you disable logging for the user/application connections, for the service provider connects and for the system itself. Each of these entities have a "Logging" tab on the configuration form. You can disable logging on this tab (Figure 2).
The second step to take is to disable persistent message queues. If the power supply and your hardware is reliable and you can afford to lose messages on power losses, you should disable persistent message queues. If persistent message queues are not enabled, the messages will not be saved to the disk, they will be stored in memory. This saves a lot of time when a message is handled. Persistent message queue handling can be disabled in the server preferences form (Figure 3) if you select Advanced tab. Then in System health you can uncheck this option.

For better performance it is also important to keep your message queues small. The reason for this is that if a message is sent and a delivery report is received it can take a lot of resources to find the appropriate message that was sent if the message queue is very large. You can keep your message queues small if you delete old messages automatically (Figure 1).
In most cases you cannot change the following, but you should know that for performance reasons it is better to:
- Use a smaller number of routing table entries
- Use a smaller number of service provider connections
- Use a smaller number of users/applications
FAQs
My messages are not received abroad. What can cause this problem?
Incorrect Number Format:
- International or roaming recipients require phone numbers in the international format. This typically starts with a plus sign (+) followed by the country code and phone number. (e.g., +441234567890)
- Double-check the formatting! You can find more details on international number formats in our FAQ section: FAQ topic about SMS number formats
- It's possible your SMS service provider might restrict sending messages to certain countries or mobile networks.
- To confirm this, contact your service provider directly. Be prepared to provide details about the specific country and mobile network where delivery is failing (e.g., "I'm trying to send messages to France using the Orange network, but they aren't being delivered").
There are errors with the error code 1365 in the log, and the messages cannot be sent. Why?
If you're encountering difficulties sending SMS messages, there could be a couple of reasons behind it. Let's break it down:
1. Incorrect Phone Number Format:
- The error might indicate an improperly formatted recipient's phone number.
- Ensure you're using the correct format:
International format: +123456789
Local format (example): 0623456789
2. Unregistered GSM Modem:
The following log lines in your system might indicate an unregistered modem:
- INFO 3344: GSM Network registration information is not available.
- INFO 3350: GSM network information:
This means your modem cannot send messages because it's not connected to the GSM network. Here are some possible causes:
- Weak or No GSM Signal: Check for a strong GSM signal in your area.
- Loose Antenna Connection: Ensure the antenna is securely connected to your modem.
- Faulty SIM Card: Try inserting the SIM card into a regular phone and attempt sending an SMS. If it fails, the SIM card might be faulty.
3. Modem Configuration Issues:
If you're confident your modem is registered, try these troubleshooting steps:
- Include Service Center (SCA) in PDU: In the "Message handling" tab of the "GSM Modem configuration form," activate the "Include Service Center (SCA) in PDU" checkbox.
- Verify SMSC Settings: Contact your service provider to confirm the correct message center address (SMSC) for your network. Update this information in the GSM modem configuration form.
- No PIN Code on SIM Card: Make sure there's no PIN code set on the SIM card. Try inserting it into another phone and see if it prompts for a PIN.
My configuration is lost after restarting the service. What can I do about this?
You might be experiencing issues with your Ozeki NG SMS Gateway if it's unable
to save configuration information. This typically occurs when the service lacks
the necessary permissions to write to the configuration directory.
To resolve this, you need to grant write access to the Ozeki NG service for the
following directory:
C:\Program Files\Ozeki\OzekiNG - SMS Gateway\config
The configuration directory stores crucial settings for your Ozeki NG. Without
write access, the service cannot save any changes you make to its configuration,
potentially causing functionality issues.
Here are a couple of ways to grant write access:
- Consult your IT Department: If you're working in a managed environment, it's recommended to involve your IT department to ensure proper permission changes are made.
- For Individual Users: If you're managing Ozeki NG on a personal computer, you can typically modify file permissions yourself through the operating system's file properties settings.
The Edit - Server Preferences, edit - Server restrictions and Driver - GSM modem 1 - Configuration winodws are all blank apart from the \'OK\' and \'Cancel\' buttons.
To experience all the features of this web application, you'll need to ensure JavaScript is enabled in your web browser. JavaScript is a programming language that powers interactive elements on websites, making them more dynamic and user-friendly.
Recommended Browser: Mozilla Firefox
For optimal performance, we recommend using Mozilla Firefox as your web browser. By default, Firefox has JavaScript enabled, so you likely won't need to make any changes.
Enabling JavaScript (if needed):
If you're using a different browser, or if you've previously disabled JavaScript in Firefox, you'll need to enable it to access the full functionality of this application. Consult your browser's specific instructions on enabling JavaScript.
Why JavaScript Matters:
JavaScript plays a crucial role in enabling interactive features like:
- Dynamic content updates without reloading the entire page
- User input validation and error handling
- Richer graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for a smooth user experience
More information
- Ozeki Cluster software
- Failover clustering (Windows Server 2012 R2)
- Failover cluster
- SMS server Backup
- SMS server Automated backup
- Manual SMS gateway uninstallation
- Manual SMS server upgrade
- Appendix
- SMS Service Provider Connectivity
- Users and SMS Applications
- Feature list of the Ozeki NG SMS Gateway
- FAQ of the Ozeki NG SMS Gateway

 Sign in
Sign in