Shared database
If you decide to store the contact details in database, the database will provide you faster access in case of large number of contacts. By default, every user in Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway is set to use separate databases. This page demonstrates how you can configure Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway to use the same database for each user.
After you configure the users in Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway to use a shared database, the users will use the same database to store their contact details, as demonstrated on Figure 1:
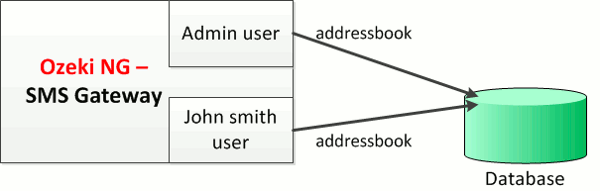
Conditions
The following operations are needed to start the configuration:
1. Install Ozeki NG SMS Gateway (for more information, click on:
Installation Steps)
2. Create Service Provider connection
Please note, that this solution is configured with MySQL database. To configure Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway's addressbook for MySQL, please follow the instructions of MySQL addressbook. Also, please note that each user has separate addressbook (for more information, click on Separate addressbook for each user) and this solution provides a solution to store each user's addressbook in the same database.
Also please note that a second user,(John Smith in this example) is installed for demonstrating purposes to provide an example for this solution. The second user can be replaced with any user in Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway.
Overview
To build up the shared database the following steps are taken in this example:
First, Install a second user (John Smith) in Ozeki NG SMS Gateway(for more information,
click on: Standard user).
After that, set the addressbook type to SQL addressbook for the each user (admin and John Smith).
Finally, customize the SQL statements.
1. General
Storing contacts in database minimizes the computer load and enables a more effective work with large amount of contacts. To set up this solution, first you need to configure each user's addressbook to store their contacts in database. For this you need to do the following:
Step 1
Click on Configure and select Advanced tab on the configuration pane. In the section called Addressbook, specify the Type of Addressbook as SQL Addressbook.
Step 2
To configure the addressbook, click on Configure and on Addressbook configuration. Select the Connection Information tab and select ODBC as connection string type.
2. Customized
As the first step of the customization, you need to contact to a database with a connection string. Please note that to connect to a database, you need to customize this connection string.
Driver={MySQL ODBC 5.1 Driver};Server=serveraddress;Database=databasename;
User=username;Password=passwd;Option=4;
|
Driver={MySQL ODBC 5.1 Driver};Server=localhost;Database=addressbook;
User=root;Password=qwe123;Option=4;
|
The database in this example is stored on the local computer (Server=localhost), I use the database named 'addressbook' (Database=addressbook), I connect with the built-in 'root' user (User=root) and its password(Password=qwe123).
User 1 - admin (user)
The first user whose addresses are stored on the database is the admin(user).
CREATE TABLE `admin_contact` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY ,
`name` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`mobile` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`telephone` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`fax` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`email` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`im` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`other` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`comm` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`createTime` DATE NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE `admin_contactGroup` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY ,
`name` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`useraccount` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`subscribekeyword` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`greetingmessage` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`unsubscribekeyword` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`byemessage` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`allowsubscription` VARCHAR( 5 ) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE `admin_membership` (
`groupId` INT NOT NULL ,
`contactId` INT NOT NULL
);
|
Click on Configure then on Addressbook configuration and select Contacts tab to customize the SQL statements as in Figure 2.
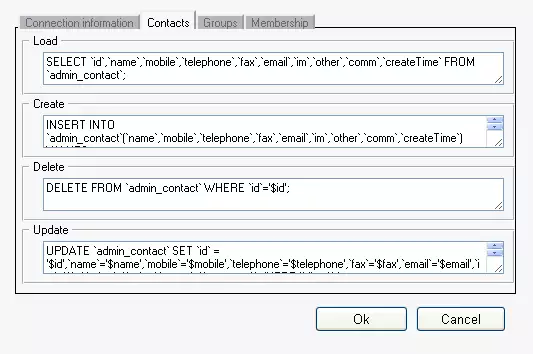
SELECT `id`,`name`,`mobile`,`telephone`,`fax`,`email`,`im`,`other`,`comm`,`createTime` FROM `admin_contact`; |
INSERT INTO `admin_contact`(`name`,`mobile`,`telephone`,`fax`,`email`,`im`,`other`,`comm`,`createTime`)
VALUES ('$name','$mobile','$telephone','$fax','$email','$im','$other','$comment','$createTime');
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID( );
|
DELETE FROM `admin_contact` WHERE `id`='$id'; |
UPDATE `admin_contact` SET `id` = '$id',`name`='$name',`mobile`='$mobile', `telephone`='$telephone',`fax`='$fax',`email`='$email',`im`='$im',`other`='$other', `comm`='$comment' WHERE `id` = $id; |
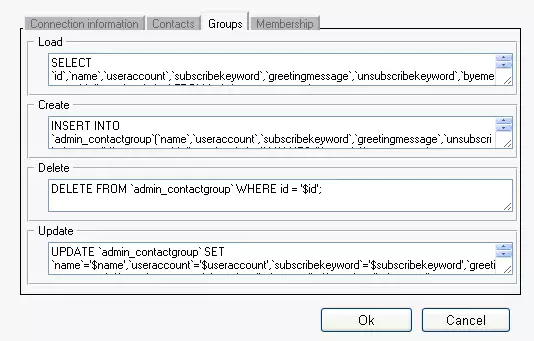
SELECT `id`,`name`,`useraccount`,`subscribekeyword`,`greetingmessage`,`unsubscribekeyword`, `byemessage`,`allowsubscription` FROM `admin_contactgroup` |
INSERT INTO `admin_contactgroup`(`name`,`useraccount`,`subscribekeyword`,`greetingmessage`,
`unsubscribekeyword`,`byemessage`,`allowsubscription`) VALUES ('$name', '$useraccount',
'$subscribekeyword', '$greetingmessage', '$unsubscribekeyword', '$byemessage',
'$allowsubscription');SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();
|
DELETE FROM `admin_contactgroup` WHERE id = '$id'; |
UPDATE `admin_contactgroup` SET `name`='$name',`useraccount`='$useraccount', `subscribekeyword`='$subscribekeyword',`greetingmessage`='$greetingmessage', `unsubscribekeyword` ='$unsubscribekeyword', `byemessage` = '$byemessage', `allowsubscription` = '$allowsubscription' WHERE `id` = '$id'; |
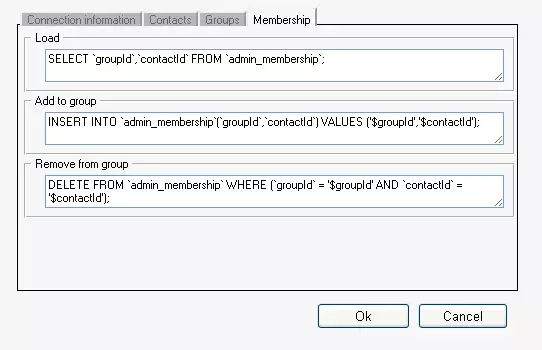
On Membership tab, perform the same as on Contacts
and Groups tabs. (Figure 4)
SELECT `groupId`,`contactId` FROM `admin_membership`; |
INSERT INTO `admin_membership`(`groupId`,`contactId`) VALUES ('$groupId','$contactId');
|
DELETE FROM `admin_membership` WHERE (`groupId` = '$groupId' AND `contactId` = '$contactId'); |
User 2 - John Smith
Other users can also store addressbooks in the same database as the admin. Take for exapmle John Smith as a user who uses the same database but different addressbook.
CREATE TABLE `john_smith_contact` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY ,
`name` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`mobile` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`telephone` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`fax` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`email` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`im` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`other` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`comm` VARCHAR( 255 ) NOT NULL ,
`createTime` DATE NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE `john_smith_contactGroup` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY ,
`name` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`useraccount` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`subscribekeyword` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`greetingmessage` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`unsubscribekeyword` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`byemessage` VARCHAR( 50 ) NOT NULL ,
`allowsubscription` VARCHAR( 5 ) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE `john_smith_membership` (
`groupId` INT NOT NULL ,
`contactId` INT NOT NULL
);
|
Click on Configure then on Addressbook configuration and select Contacts tab to customize the SQL statements.(Figure 5)
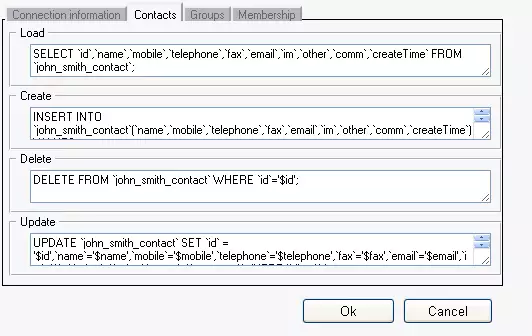
SELECT `id`,`name`,`mobile`,`telephone`,`fax`,`email`,`im`,`other`,`comm`,`createTime` FROM `john_smith_contact`; |
INSERT INTO `john_smith_contact`(`name`,`mobile`,`telephone`,`fax`,`email`,`im`,`other`,
`comm`,`createTime`) VALUES ('$name','$mobile','$telephone','$fax','$email','$im','$other',
'$comment','$createTime');SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID( );
|
DELETE FROM `john_smith_contact` WHERE `id`='$id'; |
UPDATE `john_smith_contact` SET `id` = '$id',`name`='$name',`mobile`='$mobile', `telephone`='$telephone',`fax`='$fax',`email`='$email',`im`='$im',`other`='$other', `comm`='$comment' WHERE `id` = $id; |
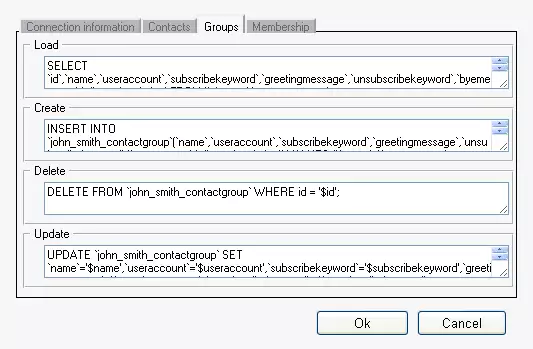
Perform the same as on Contacts tab. (Figure 6)
SELECT `id`,`name`,`useraccount`,`subscribekeyword`,`greetingmessage`, `unsubscribekeyword`,`byemessage`,`allowsubscription` FROM `john_smith_contactgroup` |
INSERT INTO `john_smith_contactgroup`(`name`,`useraccount`,`subscribekeyword`,
`greetingmessage`,`unsubscribekeyword`,`byemessage`,`allowsubscription`) VALUES
('$name', '$useraccount', '$subscribekeyword', '$greetingmessage', '$unsubscribekeyword',
'$byemessage', '$allowsubscription');SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();
|
DELETE FROM `john_smith_contactgroup` WHERE id = '$id'; |
UPDATE `john_smith_contactgroup` SET `name`='$name',`useraccount`='$useraccount', `subscribekeyword`='$subscribekeyword',`greetingmessage`='$greetingmessage', `unsubscribekeyword` ='$unsubscribekeyword', `byemessage` = '$byemessage', `allowsubscription` = '$allowsubscription' WHERE `id` = '$id'; |
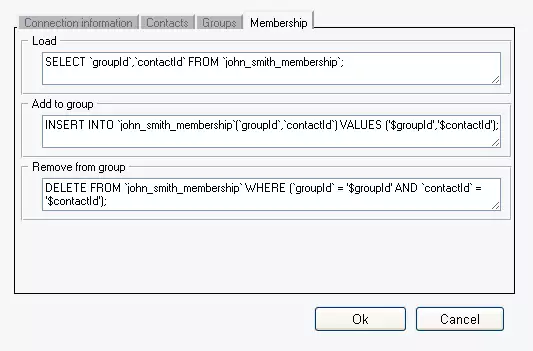
Perform the same as on Contacts and Groups tab. (Figure 7)
SELECT `groupId`,`contactId` FROM `john_smith_membership`; |
INSERT INTO `john_smith_membership`(`groupId`,`contactId`) VALUES
('$groupId','$contactId');
|
DELETE FROM `john_smith_membership` WHERE (`groupId` = '$groupId' AND `contactId` = '$contactId'); |
Conclusion
If you had followed the settings, you created a database, which is able to store user contact data. This way the Ozeki NG SMS Gateway handles a large number of contacts more efficiently, while the users use the same database but separate addressbooks.
More information

 Sign in
Sign in